What is the Limitation of the IPv4 Protocol?
News20/11/2025, 10:236 min read
What is the Limitation of the IPv4 Protocol?
Imagine your phone, laptop, or any smart gadget trying to connect to the internet without an address, pretty confusing, right? That’s exactly what IPv4 handles.
Introduced back in 1981, IPv4 gives every device a unique address so it can connect and share information. For decades, it has quietly been the backbone of the internet we use every day.
But things have changed. The internet has grown so much that IPv4 is starting to show its limits. With billions of devices online now, it’s becoming harder for IPv4 to keep up.
So, what exactly can’t it handle anymore, and why does it matter to you? Let’s take a closer look.
What is IPv4?
IPv4 sets out rules to help devices communicate online. Each device gets its own unique IP address, just like every home has its own address. If devices didn't have IP addresses, they would not be able to send, receive, or request data, effectively halting communication.
In the beginning, when there were only a few devices connected to the Internet, IPv4 worked perfectly. However, the explosion in smart devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops has increased the need for more IP addresses.
This massive increase in devices has begun to expose the deficiencies in IPv4.

Limitations of IPv4
Here are the main limitations of IPv4 explained in simple terms:
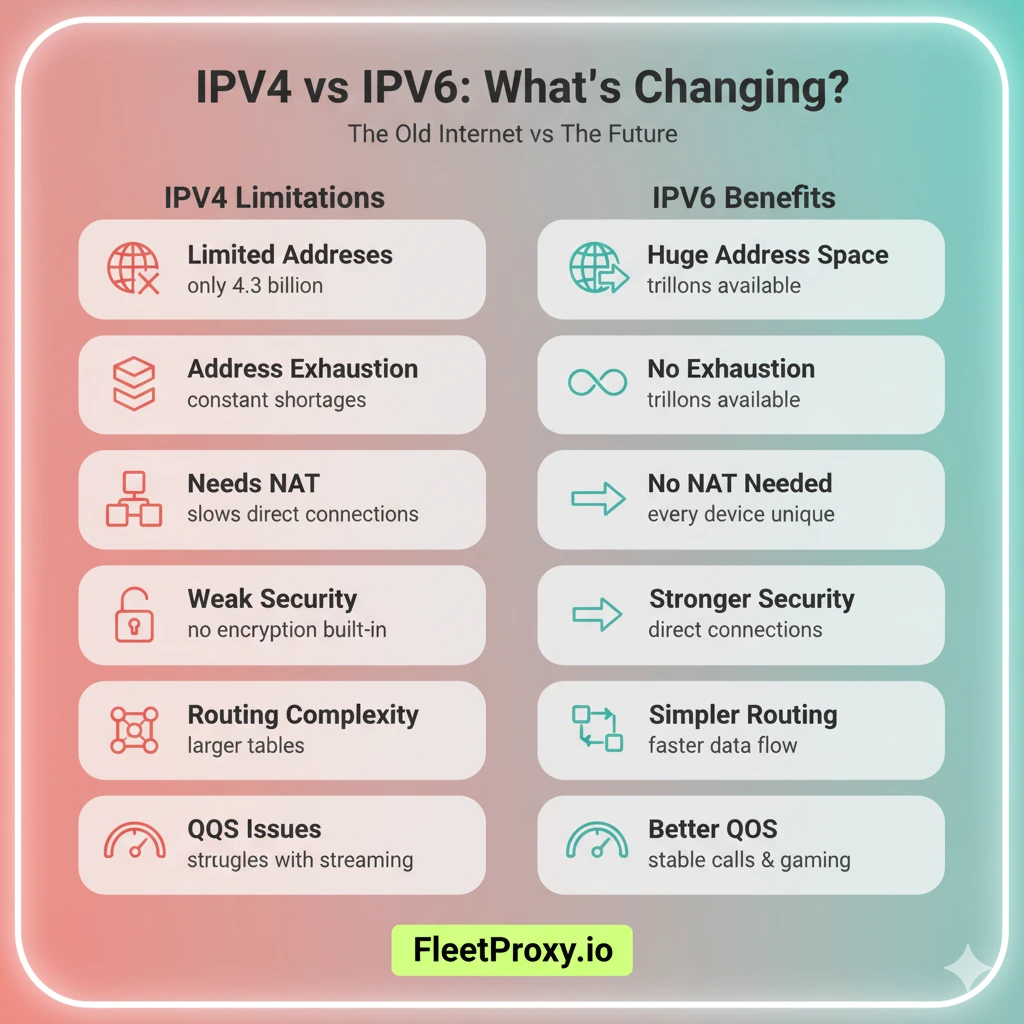
1. Limited Address Space
IPv4 offers approximately 4.3 billion unique addresses. In 1981, that seemed like a lot. Now, there are so many more devices that connect to the internet, which makes 4.3 billion addresses seem small. Some devices cannot get a unique address.
2. Address Exhaustion
All devices connected to the Internet get assigned their own unique IP addresses. IPv4 addresses are limited, which and with the rising number of devices needing new IP addresses has created an issue known "address exhaustion". This is a major problem.
3. Need for NAT
Due to a shortage of available IP addresses, networks now use NAT (Network Address Translation). NAT facilitates the sharing of a single public IP address by multiple devices.
While this is a workaround, it is definitely not a sustainable solution. It can make direct connections between devices a bit tricky and sometimes slow down the internet.
4. Security Limitations
When IPv4 was developed, security was not an issue. There are no mechanisms to protect the data, no encryption, no user authentication. This makes it easier for hackers to target networks, which is a growing concern today.
5. Routing Complexity
As the volume of data exchanged increases, routers must become more complex and use increasingly larger routing tables because this can reduce data transfer speed and even cause further slowdowns during information exchange.
6. Quality of Service (QoS) Limitations
IPv4 has difficulty tracking and prioritizing different types of internet traffic. This makes video calls, gaming, and streaming difficult, as all these activities require a fast and stable connection. Results can take a long time to arrive or can drop unexpectedly.
7. Manual Configuration
IPv4 needs some IP addresses to be set up by hand, which takes a lot of effort and is easy to mess up. In big networks, it gets a lot harder to address all the devices.
8. Geolocation Issues
IPv4 doesn’t always associate an address with the correct physical location. This can lead to issues with location-specific content and services. While trying to use geo-restricted sites or apps on the web, it can also cause mistakes.
Biggest Problem with IPv4
The main problem with IPv4 is that it is running out of addresses. As more devices connect to the Internet, unique addresses become scarcer. Also this creates complications for the growth, speed, and efficient management of large networks.

How IPv4 Limitations Are Being Solved
The leading solution is IPv6, the next version of the Internet Protocol. IPv6 offers:
• An unlimited number of addresses, enough for every device in the world.
• Better security with built-in encryption and authentication.
• Routing is simplified and the need for NAT is reduced.
IPv4 and IPv6 generally work together throughout the transition, which means that older devices can still talk to newer ones. So this helps networks stay connected as they go forward.
Conclusion
IPv4 has supported the internet for 40 years, however it has begun to show, age. With limited addresses, weak security, and complicated routing, it becomes poorly suited for today’s rapidly expanding online space.
In the long run, switching to IPv6 is the most sustainable solution, even if embracing IPv4 more is inevitable, as IPv4 is still widespread. Grasping the limits of IPv4 helps to understand the reasoning behind growth in the internet and the importance of moving to IPv6.
Understanding the challenges that lie ahead helps users and network specialists anticipate and manage the transition to an increasingly fast, secure, and dependable internet future.
More popular posts

Tips to Use a JP Web Proxy to Browse Japanese Websites Safely.
Have you ever clicked on a link to an exciting Japanese video, a regional news article, or a unique e-commerce site, only to be met with a frustrating error message? "This content is not available in your region." This digital barrier, known as geo-blocking, is a common hurdle for international fans of Japanese culture, researchers, and expats alike.

How much does an IP address cost in 2025?
The IP address cost in 2025 varies across regions. Larger blocks are cheaper per IP but costly overall, while smaller blocks offer more stability, clarity and security. No matter the option, understanding these trends helps businesses make smarter and more cost-effective decisions

How to Download Rarbg Proxies in 2025?
When RARBG went offline, it was like an era ended for torrent fans. RARBG was the most trusted place to get high-quality movies, TV shows, and games for years and it was free of the usual clutter and fake links.